New articles
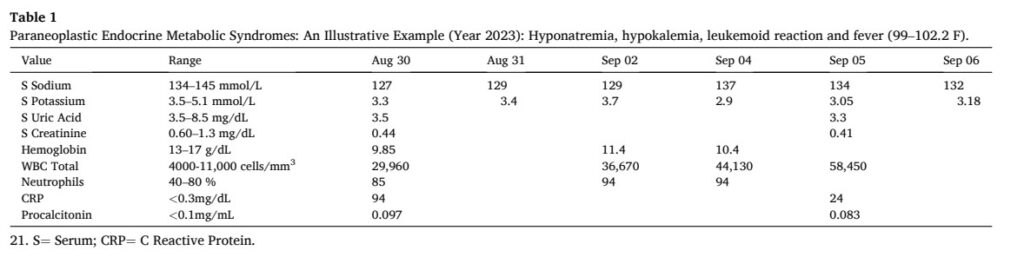
Prophylactic strategies for prevention of postpartum haemorrhage in caesarean delivery: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Methods: In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we conducted a Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating the relative effectiveness of different prophylactic agents and their combinations for postpartum haemorrhage in caesarean deliveries. We searched MEDLINE, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Embase, and Web of Science from database inception to Nov 7, 2023, for RCTs that enrolled adult pregnant women (ie, older than 18 years) undergoing a caesarean delivery; compared prophylactic strategies (monotherapy or combination drug therapy) with placebo or another active prophylactic regimen; administered prophylactic strategies of any parenteral dosage or regimen systemically before surgical incision or immediately after birth for preventing postpartum haemorrhage; and reported our prespecified endpoints of interest. Carbetocin alone and oxytocin plus tranexamic acid were superior to oxytocin monotherapy for preventing postpartum haemorrhage in caesarean deliveries. Oxytocin plus tranexamic acid ranked as the most effective intervention for postpartum haemorrhage prevention. These results are crucial in highlighting the comparative efficacy and hierarchy of prophylactic agents for postpartum haemorrhage prevention, especially given the widespread availability and low cost associated with oxytocin and tranexamic acid.
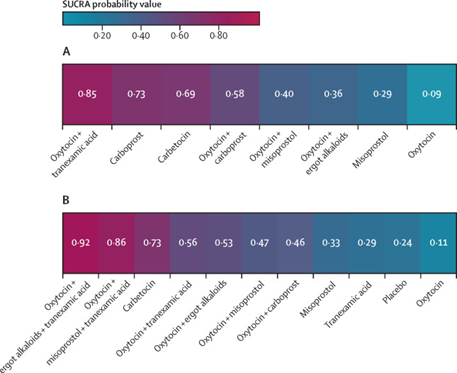
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists compared with bariatric metabolic surgery and the risk of obesity-related cancer: an observational, retrospective cohort study
Findings
Of the 6356 study participants, 3884 (61.1%) were females. At baseline, the mean age was 52.3 years (SD: 9.28), and the mean BMI was 41.5 kg/m2 (SD: 5.10). Participants were followed for a median of 7.5 years and up to 12.9 years. ORC occurred in 5.62 cases per 1000 person-years in BMS patients, and in 5.89 cases per 1000 person-years in GLP-1Ra patients; adjusted HR for GLP1-RA versus BMS 1.11 (95% CI: 0.86–1.44). Moreover, assessment of mediation through weight-loss resulted in an estimated direct effect of 41% (95% CI: 15%–59%) relative risk reduction of the pharmacotherapy.
Interpretation
Our finding suggest that first-generation GLP1-RA treatment does not increase ORC risk in patients receiving GLP1-RA treatment for diabetes and weight loss. Moreover, this may point at additional pathways beyond weight loss in which GLP-1RAs might contribute to the decreased risk for ORC, such as reducing inflammation. However, future studies, including randomized controlled trials and larger prospective cohort studies are needed to validate the observed effects and explore the underlying mechanisms.
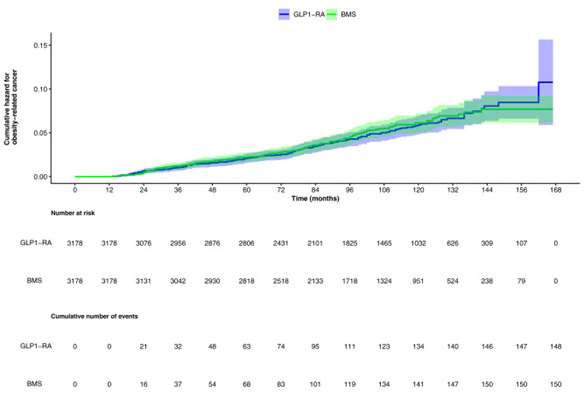
Mapping diversity in gender identity and gender roles across sex and age in the Dutch general population: a large-scale cohort study
A total of 63,190 participants (mean age = 55.4 years [SD = 12.6]) were included in the study. Most participants identified as cisgender (36,835 [58.6%; 95% CI = 58.2–58.9] cisgender women; 25,893 [41.2%; 95% CI = 40.8–41.6] cisgender men). 66 (0.11%; 95% CI = 0.08%–0.13%) participants identified as non-cisgender. Among cisgender participants registered as males, masculine gender role scores increased across age groups, with younger individuals (18–30 years) scoring lower (M = 9.3, SD = 1.2) than older individuals (71–97 years; M = 9.7, SD = 1.0; F(5,25925) = 35.5; p < 0.0001; η2 = 0.008 [95% CI = 0.006–0.010]). A similar pattern was observed for adherence to feminine gender roles among cisgender participants registered as females, where younger individuals (M = 9.1, SD = 1.2) scored lower than older individuals (M = 9.7, SD = 1.0; F(5,36900) = 137.2; p < 0.0001, η2 = 0.018 [95% CI = 0.016–0.021]). Cisgender participants registered as male reported stronger adherence to masculine roles (M = 9.6, SD = 1.0), than their female counterparts to feminine roles (M = 9.3, SD = 1.2; t(60,459)=27.7; p < 0.0001, Cohen’s d = 0.218 [95% CI = 0.202–0.234]).
Editorial
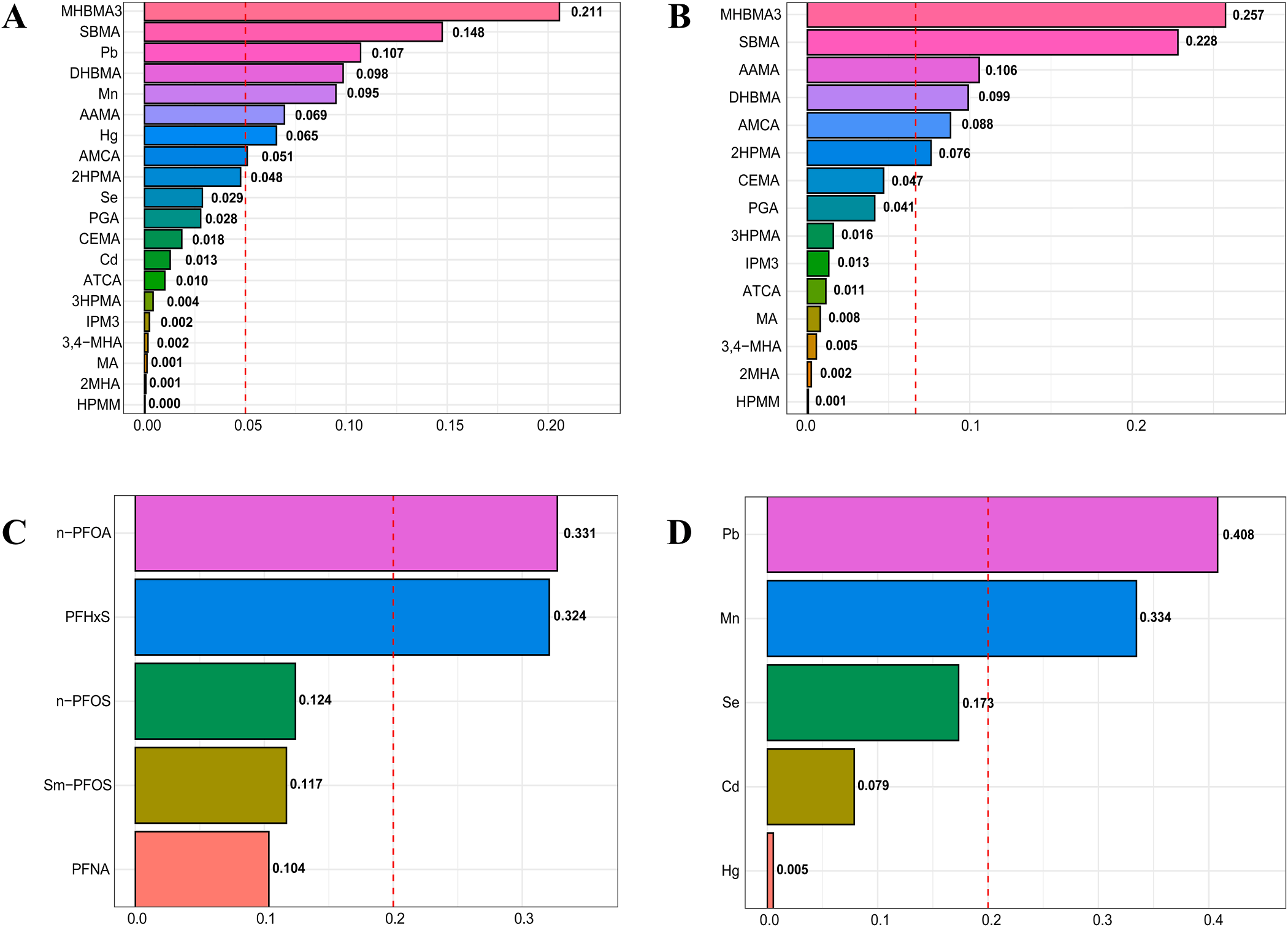
Association between endocrine disrupting chemicals exposure and diabetic kidney disease in adults
Review Association between endocrine disrupting chemicals exposure and diabetic kidney disease in adults Xinru Li a,1, Xiaoang Ye b,1 c, Luhuan Xu , Hongyu Chen d,* a Hangzhou Clinical Medical College of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, PR Chinab The Second Clinical Medical College of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University,…
Categories
General Health
Pathologies
Surgeries
Metabolic Syndrome
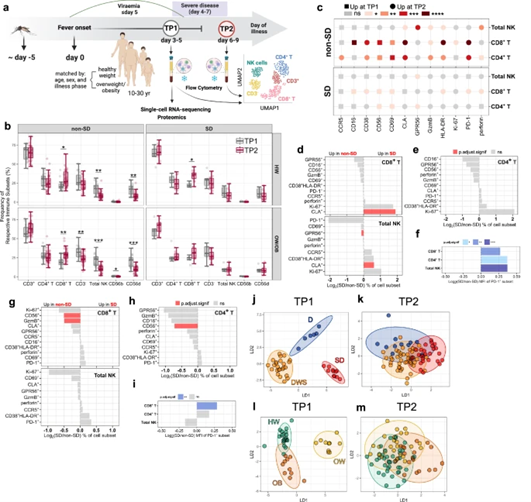
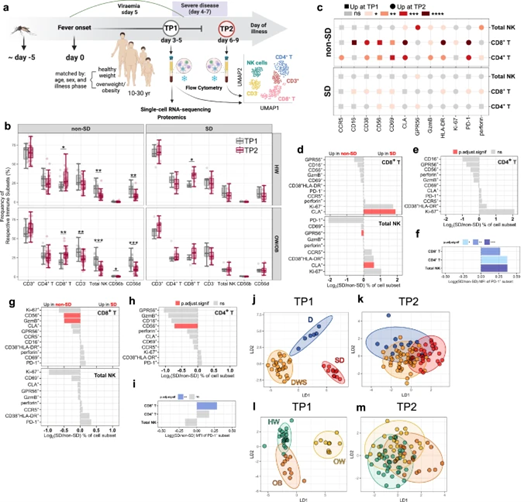
Early NK-cell and T-cell dysfunction marks progression to severe dengue in patients with obesity and healthy weight
Dengue is a mosquito-borne virus infection affecting half of the world’s population for which therapies are lacking. The role of T and NK-cells in protection/immunopathogenesis remains unclear for dengue. We performed a longitudinal phenotypic, functional and transcriptional analyses of T and NK-cells in 124 dengue patients using flow cytometry and single-cell RNA-sequencing. We show that T/NK-cell signatures early in infection discriminate patients who develop severe dengue (SD) from those who do not. These signatures are exacerbated in patients with overweight/obesity compared to healthy weight patients, supporting their increased susceptibility to SD. In SD, CD4+/CD8+ T-cells and NK-cells display increased co-inhibitory receptor expression and decreased cytotoxic potential compared to non-SD. Using transcriptional and proteomics approaches we show decreased type-I Interferon responses in SD, suggesting defective innate immunity may underlie NK/T-cell dysfunction. We propose that dysfunctional T and NK-cell signatures underpin dengue pathogenesis and may represent novel targets for immunomodulatory therapy in dengue.
Around The World
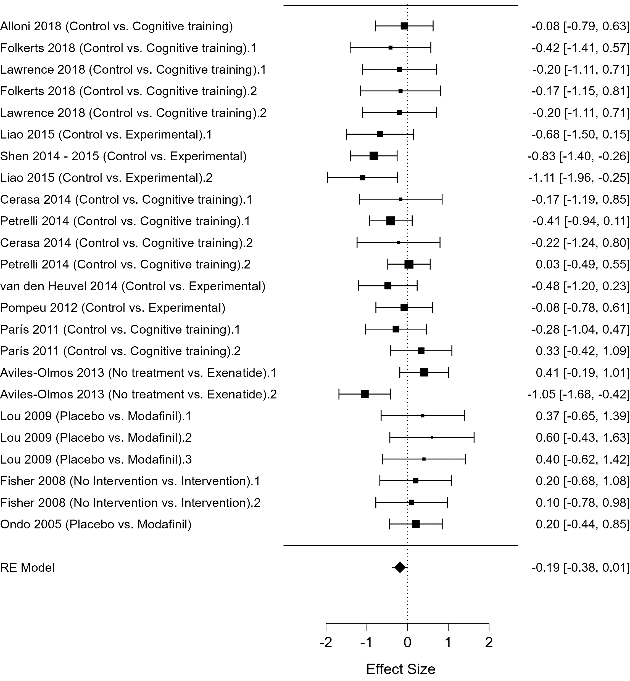
Interventions for Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease: An Umbrella Review with Meta-Analysis
Review Interventions for Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease: An Umbrella Review with Meta-Analysis Alane Medeiros Silva b, Davi Pedro Soares Macedo c, Uilna Natércia Soares Feitosa Pedro d, Edglê Pedro de Sousa Filho e b Nursing. Universidade Federal do Ceará, Ceará, Brasil. c Medicine. Faculdade Paraíso Araripina. d Nursing. Universidade de Fortaleza, Fortaleza, Brasil. e Medicine. Universidade Federal…
Podcasts
Obesity drives depot-specific vascular remodeling in male white adipose tissue
Early NK-cell and T-cell dysfunction marks progression to severe dengue in patients with obesity and healthy weight
Kupffer cell programming by maternal obesity triggers fatty liver disease