Case
Clinical challenges of paraneoplastic endocrine metabolic syndromes
Srushti Shankar , Sumal S. Sundar , Madhumati S. Vaishnav , Leena Lekkala , Chandraprabha Siddalingappa , Kavitha Muniraj , Thummala Kamala , Reshma B. Vijay , Vasanthi Nath , Mandyam D. Chitra , Pushpa Ravikumar , Siddartha Dinesha , Tejeswini Deepak , Srikanta Sathyanarayana *
Samatvam Diabetes Endocrinology and Medical Centre, Samatvam: Science and Research for Human Welfare Trust, Bangalore, India
ARTICLE INFO
Edited by Dr G Liu
Keywords:
Endocrine metabolic paraneoplastic syndromes Paraneoplastic hyponatremia
Paraneoplastic leukemoid reaction Paraneoplastic hypokalemia Paraneoplastic fever
Highlights
- Recognition of these diverse clinical manifestations improves clinical outcomes (earlier cancer diagnosis, better quality of life, optimal tumour-directed therapy or decision towards non-aggressive focussed palliative care).
ABSTRACT
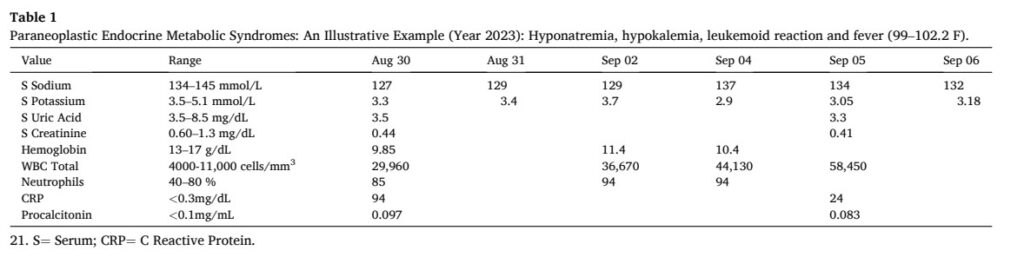
Background/objective: Paraneoplastic endocrine metabolic syndromes are rare, but clinically significant mani- festations of underlying malignancies, often complicating clinical course and impacting treatment outcomes. Case presentation: Four different paraneoplastic syndromes manifested in an 81-year-old female with metastatic carcinoma rectum, presenting with generalized weakness, inability to walk, severe pain, and low-grade fever.
Discussion: Endocrine metabolic paraneoplastic syndromes can impact prognosis and even be confused as met- astatic spread or another “non-existent” clinical entity. They can precede, occur concomitantly or present at later stage of tumour development.
Conclusion: Recognition of these diverse clinical manifestations improves clinical outcomes (earlier cancer diagnosis, better quality of life, optimal tumour-directed therapy or decision towards non-aggressive focussed palliative care).
Article
Paraneoplastic Hypokalemia: Hypokalemia (2.9, 3.0), likely due to intracellular potassium uptake (in vivo/in vitro) by rapidly prolif- erating leukocytes and primary/metastatic neoplastic cells (ectopic ACTH secretion ruled out) was treated with intravenous/oral po- tassium supplementation.
The objective of this study was to conduct a meta-analysis of interventions in Parkinson’s disease, synthesizing evidence across motor and non-motor outcomes, including cognition, depression, sleep, fatigue, gait parameters, and quality of life.
Available online 25 July 2025
0147-6513/© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. This is an open access article under the CC BY license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).